What is Passivation?
Passivation is a non-electrical metal finishing technique used to prevent corrosion and pitting in metal surfaces. By removing free iron and other contaminants, passivation helps restore the material to its original condition and strengthens it against corrosion. It is particularly effective for stainless steel, which contains chromium and nickel, elements that contribute to its corrosion resistance.
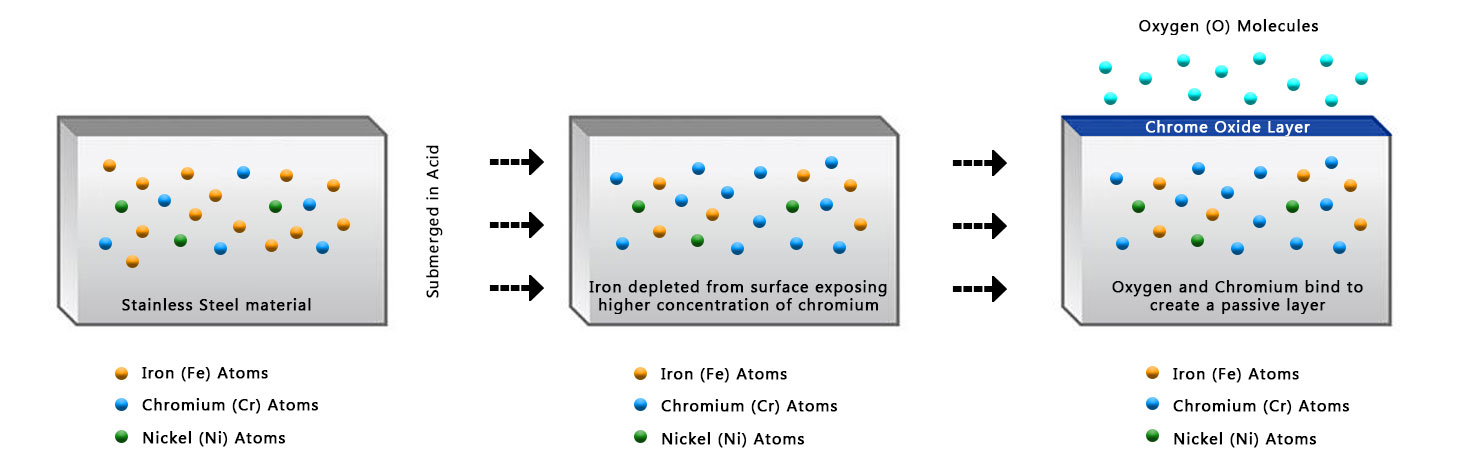
The passivation process involves immersing stainless steel parts in a bath of nitric or citric acid-based solution. The acid concentration, temperature, and duration of the treatment are carefully controlled to remove surface contaminants and promote the formation of a protective oxide layer. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing corrosive substances from reaching the metal surface.
Why is Passivation Essential for Stainless Steel?
Passivation is essential for stainless steel because it helps enhance its corrosion resistance properties. Stainless steel contains a thin passive film on its surface made primarily of chromium oxide. This film is what gives stainless steel its corrosion-resistant properties. However, during manufacturing processes such as welding, machining, or forming, this passive film can be damaged or contaminated with foreign materials.
Passivation is a process wherein the stainless steel surface is treated to remove contaminants and restore the passive film. This process typically involves cleaning the surface thoroughly and then immersing it in a passivating solution, usually a nitric acid solution. The nitric acid removes any iron contamination or embedded particles and facilitates the formation of a fresh, protective chromium oxide layer.
Without passivation, the stainless steel might be more susceptible to corrosion, particularly in harsh environments or under certain conditions. Passivation ensures that the stainless steel maintains its corrosion resistance and extends its service life, making it suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, food processing, and medical devices.
Benefits of Passivation
- ✓ Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
- ✓ Removes Surface Contamination
- ✓ Reduces the Risk of Product Contamination
- ✓ Restoration of Metal Integrity
- ✓ Uniform and Smooth Finish
- ✓ Save Money and Reduces Downtime
Factors Affecting Passivation Efficacy
Numerous factors can impact the passivation of stainless steel surfaces, preventing the efficacy of the process. Below are some of these factors:
Environmental Influences
The temperature at which stainless steel is passivated determines the efficacy of the process. Temperature plays a vital role in passivation because a higher temperature makes the method more effective. Similarly, high chloride levels in cleaning agents and salt water can cause crevice corrosion in passivated stainless steel.
Material Composition
The composition of the alloy is another factor that usually influences the efficacy of the passivation finish treatment. These materials may contain different levels of alloying elements, including nickel, molybdenum, and chromium, affecting the oxide film’s formation and firmness. In some cases, the machining residues or other surface contaminants on the material affect the passivation’s efficiency.
Post-Passivation Treatment
Extracting the material from the acid bath at the due time is advisable to achieve the desired oxide layer thickness. Then, it is important to rinse and dry it to remove leftover solution or contaminants properly. Ensure to dry the surface properly to avoid water spots or contaminating the surface.
